Understanding Ulcers: Types, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction:
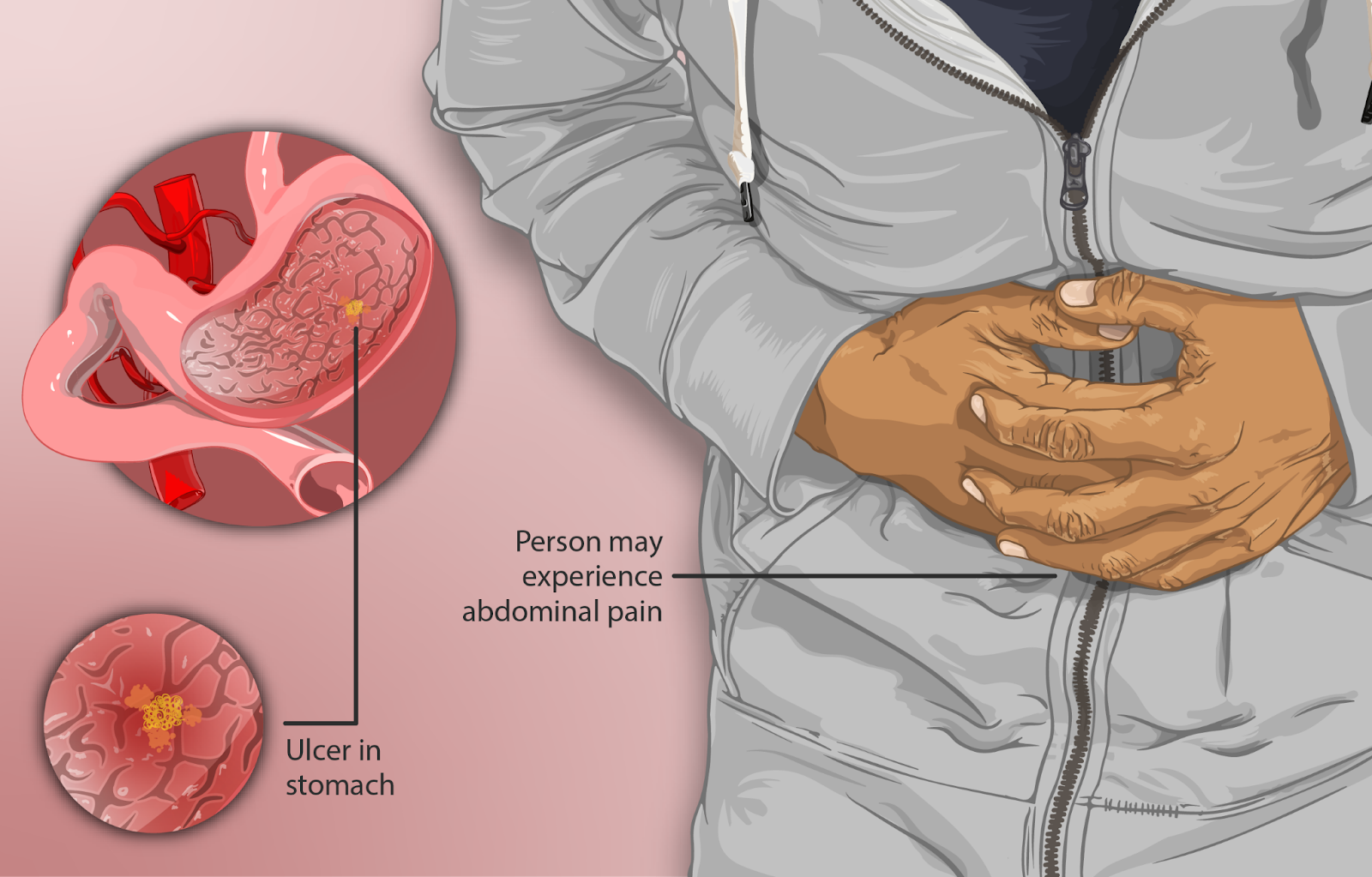
Types of Ulcers:
a) Peptic Ulcers: These ulcers occur in the stomach or the first part of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. Peptic ulcers frequently occur in connection with the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) or the utilization of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). These ulcers are characterized by a burning pain in the abdomen, bloating, nausea, and heartburn.
b) Mouth Ulcers: Also known as canker sores, these ulcers occur in the mouth and can be triggered by factors like stress, injury, or certain dietary deficiencies. They typically present as round or oval-shaped sores with a white or yellowish center and a red border.
c) Venous Ulcers: Venous ulcers are a type of leg ulcer that develop due to poor blood circulation in the veins, usually in the lower leg or ankle. They are often associated with conditions like chronic venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis, or varicose veins. These ulcers typically present as open sores with a weeping or shiny appearance.
d) Pressure Ulcers: Also known as bedsores, pressure ulcers develop due to prolonged pressure on the skin and underlying tissues. They commonly affect individuals who are bedridden, wheelchair-bound, or have limited mobility. Pressure ulcers can range from mild inflammation to severe wounds that penetrate through the skin and underlying tissues.
Responsible Factors for Ulcers:
Several factors can contribute to the development of ulcers, depending on the type. Some common responsible factors include:
a) Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Infection: This bacterial infection is a major cause of peptic ulcers. H. pylori damages the protective lining of the stomach and small intestine, making them more susceptible to acid damage.
b)Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Prolonged use of NSAIDs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, can irritate the stomach lining and increase the risk of peptic ulcers.
c) Stress: Emotional and psychological stress can exacerbate or trigger mouth ulcers.
d) Poor Circulation: Venous ulcers are often caused by conditions that impair blood flow in the veins, such as obesity, deep vein thrombosis, or varicose veins.
e) Immobility: Pressure ulcers commonly develop in individuals who are confined to a bed or wheelchair for extended periods, as constant pressure on certain areas can cause tissue damage.
Prevention and Treatment: Preventing and treating ulcers involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and, in some cases, medical interventions.Here are several strategies for prevention and various therapeutic approaches:
a) Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication: If an H. pylori infection is detected, a course of antibiotics is usually prescribed to eliminate the bacteria. This treatment is crucial in preventing the recurrence of peptic ulcers.
b) Limit NSAID Usage: If possible, reducing the use of NSAIDs or finding alternative pain management methods can help prevent peptic ulcers. If NSAIDs are necessary, taking them with food or using a protective medication, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), can help minimize the risk of ulcers.
c) Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or counseling, can help prevent or manage mouth ulcers triggered by stress.
d) Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can contribute to ulcer prevention. These include avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise.
e) Healthy Diet: A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in preventing and managing ulcers. Here are some dietary considerations:
1.Avoid Trigger Foods: Spicy foods, acidic foods, and caffeinated beverages can irritate the stomach and exacerbate symptoms. It is recommended to minimize or restrict their intake.
2 .Eat Smaller, Frequent Meals: Instead of consuming large meals, opt for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This helps reduce the strain on the digestive system and prevents excessive acid production.
3 .Include High-Fiber Foods: Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, help promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation, which can worsen ulcers.
4 . Probiotics: probiotics, found in yogurt and fermented foods, can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which may aid in preventing H. pylori infections and promoting gut health.
5 .Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day helps maintain the integrity of the stomach lining and supports overall digestive health.
Medications: Depending on the type and severity of the ulcer, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to manage symptoms or aid in the healing process. These may include antacids to neutralize stomach acid, H2 blockers to reduce acid production, or PPIs to inhibit acid secretion.
In addition to these preventive measures and treatment options, it is crucial to follow your healthcare provider's advice, attend regular check-ups, and promptly seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms.
Conclusion: Ulcers can significantly impact an individual's well-being, causing discomfort and pain. However, with proper understanding, preventive measures, and appropriate treatment, ulcers can be effectively managed and their recurrence minimized. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, making dietary adjustments, managing stress, and following medical advice are key to preventing and treating ulcers. Remember to consult your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan based on your specific condition.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace any professional medical advice.









0 Comments